
The Transfer Coating Machine is a crucial innovation in various manufacturing sectors. Industry reports indicate that the market for these machines is projected to grow significantly, with estimates reaching $5 billion by 2025. This surge reflects an increasing demand for advanced coating solutions that enhance product performance.
At its core, a Transfer Coating Machine applies thin layers of material onto surfaces. This process is vital in electronics, automotive, and medical industries. With precision and efficiency, these machines reduce waste and improve manufacturing productivity. However, there are challenges. Manufacturers must ensure optimal adhesion and consistency in application.
In practice, the Transfer Coating Machine operates through complex systems involving heat and pressure. The technology allows for intricate designs and textures on various substrates. Yet, maintaining quality can be difficult. Sometimes, errors in coating can lead to product failures. Continuous improvement in machine technology and user training can address these issues, ensuring better outcomes.

A transfer coating machine is a specialized device used in various industries. It applies coatings, such as paints or adhesives, onto different substrates. This machine is crucial for enhancing surface properties and achieving specific aesthetic effects.
In operation, the machine uses a transfer technique to ensure uniform coating. Substrates pass through rollers that apply the coating, ensuring consistent thickness. After coating, substrates often undergo drying or curing processes. Precise control is essential for quality finishes.
Tips: Regular maintenance is crucial. Check for wear on rollers and replace them as needed. Clean the machine to prevent cross-contamination between different coatings.
When using a transfer coating machine, consider the substrate material. Different materials may require unique adjustments to the process. Test a small section first to ensure desired results. The equipment can sometimes be challenging, and adjustments may lead to imperfect outcomes. Always be ready to refine your techniques.
Transfer coating machines play a crucial role in various manufacturing sectors. They primarily function by applying a coating from one substrate to another. This transfer process often involves the use of heat and pressure. However, the consistent quality of the final product can be challenging to achieve. Improper settings may lead to uneven coatings.
The operation principles of transfer coating machines are built around specific techniques. A roller or belt transports the substrate coated with the desired material. During this process, the coating is pressed onto the target surface. Temperature control is vital here. Too low or too high can compromise adhesion and finish. Many operators face difficulties in getting this balance right.
Furthermore, these machines require regular maintenance to work effectively. Neglecting upkeep may lead to downtime or quality issues. Often, the team must rebuild or recalibrate components to maintain efficiency. Each machine's design influences its operational principles. Understanding these intricacies can improve performance and reduce waste. Adapting techniques based on production needs can lead to better outcomes.
Transfer coating machines play a crucial role in various industrial sectors. These machines apply coatings onto surfaces, enhancing their durability and aesthetic appeal. To understand how they function, it's essential to look at their key components.
The primary element is the coating unit. This unit applies a specialized transfer medium onto the substrate. It ensures a uniform layer, but inconsistencies can occur. Sometimes, the thickness may vary unexpectedly. This inconsistency can affect final product quality, prompting the need for careful calibration.
Another vital component is the drying system. After coating, the surface must dry properly. If the drying process fails, it can lead to imperfections. Uneven drying can result in bubbling or peeling. Regular maintenance and adjustments are important to prevent these issues. It's a balancing act, ensuring efficiency and quality without overlooking potential flaws. Proper training for operators can help minimize errors during these processes.
| Component | Function | Material Used | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coating Unit | Applies the coating material to the substrate | Polymer, Paint | Manufacturing, Automotive |
| Heating System | Cures the applied coating for adhesion | Infrared, Hot air | Electronics, Furniture |
| Cooling Unit | Lowers the temperature post-coating to stabilize | Air, Chilled water | Textiles, Plastics |
| Control System | Manages the operation and parameters of the machine | Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) | All sectors using automation |
| Substrate Feed Mechanism | Feeds substrate material into the coating area | Conveyor belts, Rollers | Packaging, Wood processing |
Transfer coating technology offers versatile applications across various industries. One area benefiting from this technology is automotive manufacturing. Transfer coating can enhance surfaces of parts like bumpers and panels. It provides a protective layer while reducing weight. This process helps manufacturers achieve better fuel efficiency. However, achieving uniform thickness can sometimes be challenging.
Another key application lies in electronics. Transfer coating helps in producing intricate patterns on circuit boards. It allows for precise placement of conductive materials. This precision is crucial for the performance of modern electronics. Yet, controlling the adhesion level remains a significant consideration. Getting it just right demands careful calibration and testing.
In the textile industry, transfer coating is also notable. It adds designs or patterns onto fabrics with ease. This method enhances aesthetic appeal while preserving fabric softness. However, the durability of the design can vary. This inconsistency may require further exploration and improvements. Overall, transfer coating technology continues to evolve. Each application presents unique challenges, prompting innovation and reassessment of techniques.
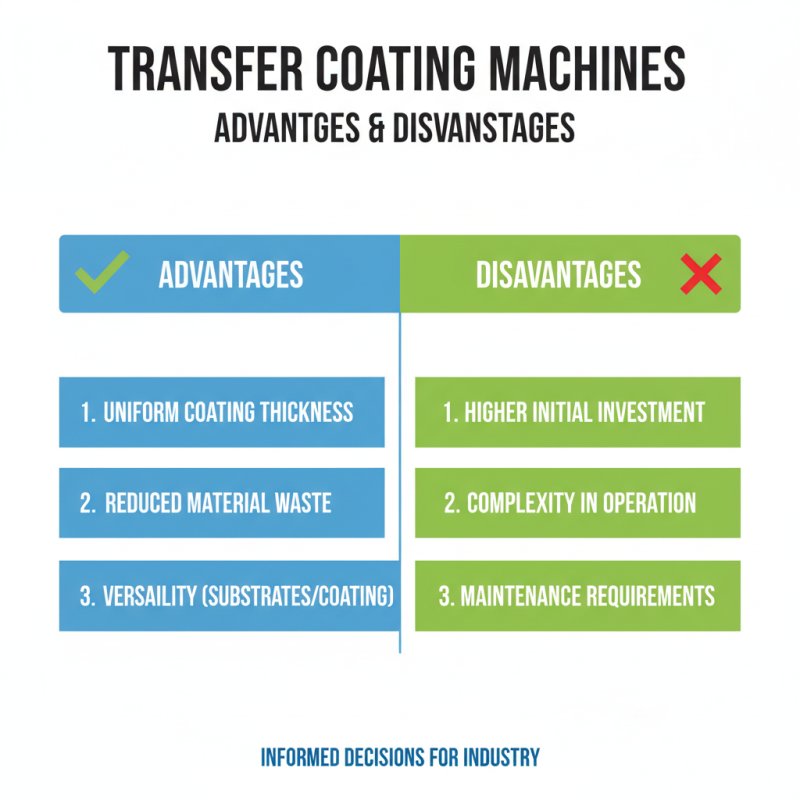
Transfer coating machines are gaining popularity in various industries. They offer significant advantages but come with some drawbacks. Understanding these can help businesses make informed decisions.
One key advantage is efficiency. According to recent industry reports, companies can reduce production time by up to 30% when using these machines. They enable fast applications of coatings on different surfaces. This speed can lead to higher output rates. However, the initial costs can be high. Smaller companies may struggle to invest in this technology.
Another benefit is the precision of the coating process. Transfer coating machines allow for uniform application, which minimizes material waste. Yet, this precision requires proper calibration. If not set correctly, the coating may not adhere as expected, leading to rework. Additionally, the versatility of these machines makes them suitable for various materials. But, adapting them for specific materials can be challenging.
Ultimately, weighing these pros and cons is crucial. While the potential for efficiency is great, the challenges should not be overlooked.





